SQL Server Queries
Creating a new table
Syntax: create table table name
create table products (id int, name varchar(50),price money)
Inserting values into table
insert into products (id,name,price)
values (1,'aa',12),(2,'bb',15),(3,'cc',45),(4,'dd',6),(5,'ee',9),(6,'ff',65)
Displaying all columns in a table
select*from products - This query displays all the columns of table named products
Sorting the records in descending order
select id,name,price from products
order by name desc
Note: For ascending order there is no need to mention asc i.e. if we give
order by name, that itself orders in ascending order.
Displaying first 3 Records
select top 3 * from products
To select a particular record using WHERE clause
select name, price from products
where price = 65
Here we are using WHERE condition to select a particular record - Price equal to 65.
To display the records where the price less than or equal to 45
select name, price from products
where price <= 45
order by price
Note: Take a look at the price wise ascending order

To display all the records except the values equal to 'ee', 'ff'.
This can be achieved by using NOT EQUAL TO (< >) as well as AND operator.
select * from products
where name <> 'ee' AND name <>'ff'Similarly, we can also use != as not equal to operator. For ex, the following query displays all the records except the record 'aa'.
select *from products
where name! = 'aa'---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Between Operator is used to select the values within a given range. For example, between two dates,
between two values etc.
select *from products
where price BETWEEN 6 AND 12
order by price
Here we are selecting the price values in between 6 and 12.
Checking for NULL values
select *from products
where price is NULL
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
In operator
Suppose we need to fetch multiple records. In order to do that we have to use IN operator
select * from products
where name in ('aa','cc','ff')
OR operator
select * from products
where name = 'bb' OR name = 'dd'
OR operator displays a record if either the first condition OR the second condition is true.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NOT condition
Not condition is one of a logical operator which negates or inverts a condition i.e. it produces the reverse of a condition. For example, if we
want to find out the names of the players who do not play hockey, then the query would be look like this,
SELECT names,games FROM players
where NOT games = 'hockey'
The output would be something like:
names games
Sam football
Richard football
Billy volleyball
Julie Badminton
select * from products
where NOT name = 'aa' AND NOT name = 'bb' AND NOT name = 'gg'
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
LIKE operator (wildcards)
The Like
operator compares a value or a character to similar values or characters with
the help of wildcard operators.
Here,
the percent sign (%) represents zero, one or multiple characters. Therefore,
this % wildcard matches one or more characters and displays the matching
records.
select * from products
where name like 'd%'
% Wildcard
select * from products
where name like 'c%'
[] Wildcard
select * from products
where name like '[cd]%'
Wildcard with ^ carat symbol negates
the above bracket wildcard
select * from products
where name like '[^cd]%'
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Inserting values into a column named quantity
insert into products (quantity)
values (2),(3),(5), (6)
delete from products
where quantity in (3,5)
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Distinct keyword
select
* from salary
The distinct keyword fetches the unique records from the group of records having many identical records (also called as duplicates).
The above table has many duplicate values in salary column. Therefore, by using the distinct keyword, we can fetch the records having unique values.
select distinct salary
from salary
Average Function
select avg (distinct salary) AS avg_salary
from salary
The above query returns the average salary
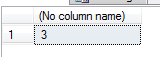
Count ()
function
select count (*) from salary
The above query returns the number of records from a table named 'salary'
Count (distinct
column name)
select count (distinct salary) from salary
To change the
old table name with the new table name
sp_RENAME 'joins’, 'customers'





















No comments:
Post a Comment